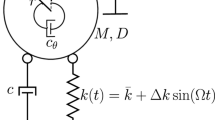Abstract
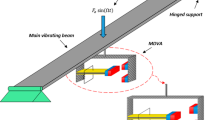
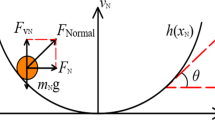
Prior to the design and fabrication of MEMS/NEMS devices, analysis of static and dynamic behaviors of these systems is necessary. In the present study, the nonlinear dynamic behavior of micro- and nano-mechanical resonators is investigated and classified based on the resonator’s physical parameters for first time. The Galerkin method is used to convert the distributed-parameter model to a nonlinear ordinary differential equation where mid-plane stretching, axial stress, DC electrostatic and AC harmonic voltages are taken into account. To obtain the analytical frequency response of the micro resonator near its primary resonance, the second order multiple scales method is applied to the general equation of motion with cubic, quadratic and parametric nonlinearities. It is demonstrated that variation of the micro resonator’s physical parameters strongly affects its dynamic behavior by changing equilibrium points and their stability properties and complex behaviors appear in its frequency and phase responses. The global dynamics of the resonator is classified into four different categories in terms of the system parameters in this paper. The dynamic characteristics and frequency response of each class are analyzed numerically as well as analytically. Comparison of the obtained closed-form solution with the numerical simulation results confirms its validity. A striking point of the obtained closed-form solution is that it predicts some complex nonlinear behaviors of the resonator. This paper presents a quick and efficient method for determining the global dynamics of the micro-resonators and can be useful in design and analyses of these devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azgin K, Akin T, Valdevit L (2012) Ultrahigh-dynamic-range resonant MEMS load cells for micromechanical test frames. Microelectromech Syst J 21(6):1519–1529
Baghani M (2012) Analytical study on size-dependent static pull-in voltage of microcantilevers using the modified couple stress theory. Int J Eng Sci 54:99–105
Belardinelli P et al (2013) Dynamical characteristics of an electrically actuated microbeam under the effects of squeeze-film and thermoelastic damping. Int J Eng Sci 69:16–32
Dohn S et al (2005) Enhanced functionality of cantilever based mass sensors using higher modes. Appl Phys Lett 86(23):233501
Erbe A et al (2000) Mechanical mixing in nonlinear nanomechanical resonators. Appl Phys Lett 77(19):3102–3104
Fakhrabadi MMS, Rastgoo A, Ahmadian MT (2013) Dynamic behaviours of carbon nanotubes under dc voltage based on strain gradient theory. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(40):405101
Haghighi HS, Markazi AH (2010) Chaos prediction and control in MEMS resonators. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(10):3091–3099
Hajjam A, Pourkamali S (2012) Fabrication and characterization of MEMS-based resonant organic gas sensors. Sens J IEEE 12(6):1958–1964
Hassanpour PA et al (2010) Nonlinear vibration of micromachined asymmetric resonators. J Sound Vib 329(13):2547–2564
Hu Y, Yang J, Kitipornchai S (2010) Pull-in analysis of electrostatically actuated curved micro-beams with large deformation. Smart Mater Struct 19(6):065030
Jia X et al (2012) Resonance frequency response of geometrically nonlinear micro-switches under electrical actuation. J Sound Vib 331(14):3397–3411
Joglekar M, Pawaskar D (2011) Closed-form empirical relations to predict the static pull-in parameters of electrostatically actuated microcantilevers having linear width variation. Microsyst Technol 17(1):35–45
Kacem N et al (2009) Nonlinear dynamics of nanomechanical beam resonators: improving the performance of NEMS-based sensors. Nanotechnology 20(27):275501
Lakrad F, Belhaq M (2010) Suppression of pull-in instability in MEMS using a high-frequency actuation. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(11):3640–3646
Mestrom R et al (2008) Modelling the dynamics of a MEMS resonator: simulations and experiments. Sens Actuators A 142(1):306–315
Miandoab EM et al (2014a) Polysilicon nano-beam model based on modified couple stress and Eringen’s nonlocal elasticity theories. Physica E 63:223–228
Miandoab EM, Yousefi-Koma A, Pishkenari HN (2014b) Nonlocal and strain gradient based model for electrostatically actuated silicon nano-beams. Microsyst Technol 21(2):457–464
Miandoab EM, Pishkenari HN, Yousefi-Koma A (2014) Chaos predition in MEMS-NEMS resonators. Int J Eng Sci 82:74–83
Mojahedi M et al (2011) Analytic solutions to the oscillatory behavior and primary resonance of electrostatically actuated microbridges. Int J Struct Stab Dyn 11(06):1119–1137
Nayfeh AH, Mook DT (2008) Nonlinear oscillations. Wiley, New York
Palaniapan M, Khine L (2008) Nonlinear behavior of SOI free-free micromechanical beam resonator. Sens Actuators A 142(1):203–210
Rocha LA et al (2011) Auto-calibration of capacitive MEMS accelerometers based on pull-in voltage. Microsyst Technol 17(3):429–436
Sharma M et al (2012) Parametric resonance: Amplification and damping in MEMS gyroscopes. Sens Actuators A 177:79–86
Siewe MS, Hegazy UH (2011) Homoclinic bifurcation and chaos control in MEMS resonators. Appl Math Model 35(12):5533–5552
Timurdogan E et al (2011) MEMS biosensor for detection of Hepatitis A and C viruses in serum. Biosens Bioelectron 28(1):189–194
Tocchio A, Caspani A, Langfelder G (2012) Mechanical and electronic amplitude-limiting techniques in a MEMS resonant accelerometer. Sens J IEEE 12(6):1719–1725
Wen-Hui L, Ya-Pu Z (2003) Dynamic behaviour of nanoscale electrostatic actuators. Chin Phys Lett 20(11):2070
Younis MI (2011) MEMS linear and nonlinear statics and dynamics, vol 20. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Younis M, Nayfeh A (2003) A study of the nonlinear response of a resonant microbeam to an electric actuation. Nonlinear Dyn 31(1):91–117
Younis M et al (2010) Nonlinear dynamics of MEMS arches under harmonic electrostatic actuation. Microelectromech Syst J 19(3):647–656
Zhang L, Zhao Y-P (2003) Electromechanical model of RF MEMS switches. Microsyst Technol 9(6–7):420–426
Zhang Y, Zhao Y-P (2006) Numerical and analytical study on the pull-in instability of micro-structure under electrostatic loading. Sens Actuators A 127(2):366–380
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Murphy KD (2012) Nonlinear dynamic response of beam and its application in nanomechanical resonator. Acta Mech Sin 28(1):190–200
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miandoab, E.M., Pishkenari, H.N. & Yousefi-Koma, A. Nonlinear dynamics of nano-resonators: an analytical approach. Microsyst Technol 22, 2259–2271 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2657-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2657-6